Welcome to our article on understanding dropping pregnancy hormone levels. Pregnancy is an incredible journey filled with various physiological changes, and hormones play a crucial role in supporting a healthy pregnancy. However, it’s not uncommon for pregnant women to experience a decrease in hormone levels during the early stages of pregnancy, which can have effects on the pregnancy itself.
When pregnancy hormone levels drop, it may raise concerns and questions about the impact on both the mother and the baby. In this article, we will explore the reasons why pregnancy hormone levels can decrease, the potential effects of low hormone levels on the pregnancy, and how to manage hormone imbalances to ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome.
Understanding the intricacies of dropping pregnancy hormone levels can help expectant mothers navigate any potential challenges and seek appropriate support and guidance from healthcare providers.
Key Takeaways:
- During early pregnancy, it is possible for pregnancy hormone levels to drop.
- Low hormone levels can have effects on the progress and outcome of the pregnancy.
- Managing hormone imbalances is important for a healthy pregnancy.
- Seeking advice from healthcare providers is crucial for understanding and addressing hormone fluctuations.
- Research and medical advancements are continuously being made to improve support for women experiencing hormone changes during pregnancy.
Hormonal Changes in Early Pregnancy
During the early stages of pregnancy, the female body undergoes numerous hormonal changes to support the development and growth of the fetus. These changes are essential for a healthy pregnancy but can also lead to fluctuations in hormone levels. Understanding the hormonal changes in early pregnancy and the causes of declining hormone levels is crucial for expectant mothers and healthcare providers.
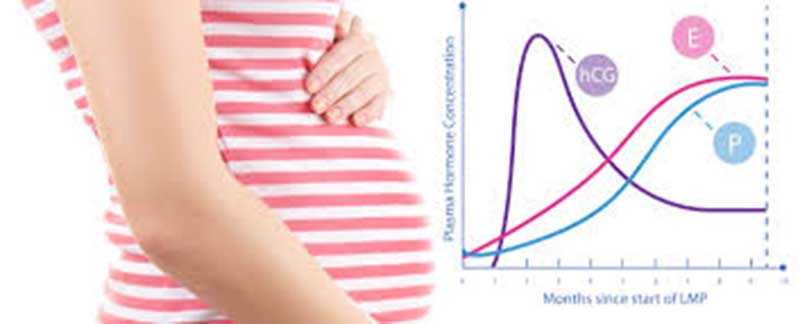
Several hormones play a significant role in pregnancy, including human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), progesterone, and estrogen. These hormones work together to create an optimal environment for the embryo to implant and grow. However, it is common for hormone levels to fluctuate during the first trimester.
The exact causes of declining hormone levels during pregnancy can vary. One of the primary factors is the placenta taking over hormone production from the ovaries. As pregnancy progresses, the placenta becomes more capable of producing the necessary hormones, relieving the dependence on the ovaries. This transition can lead to a decrease in hormone levels, particularly in estrogen and progesterone.
“The hormone levels in early pregnancy can be influenced by various factors. While a decline in hormone levels may be a normal part of the pregnancy process, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for guidance and support,” advises Dr. Rachel Johnson, a renowned obstetrician-gynecologist.
| Hormone | Function |
|---|---|
| Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) | Supports implantation and viability of the pregnancy |
| Progesterone | Maintains the uterine lining and prevents contractions |
| Estrogen | Stimulates uterine blood flow and fetal development |
It is important to note that not all hormonal changes in early pregnancy will lead to complications. While declining hormone levels can be a natural part of the process, persistent or severe drops in hormone levels may require medical attention. It is vital for expectant mothers to be aware of any unusual symptoms and seek professional advice.
In the next section, we will explore the potential symptoms of declining hormone levels during pregnancy. Understanding these symptoms can help women monitor their health and seek appropriate care when needed.
Symptoms of Decreasing Hormone Levels
In early pregnancy, it is not uncommon for hormone levels to fluctuate. However, when these hormone levels start to drop significantly, it can lead to various symptoms that women may experience. These symptoms can manifest as both physical and emotional changes, signaling potential imbalances in hormone levels.
Physical Symptoms:
- Spotting or light bleeding: A decrease in hormone levels may cause vaginal bleeding or spotting, which should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
- Abdominal discomfort: Some women may experience abdominal pain or cramping as a result of hormonal fluctuations.
- Breast changes: Hormone imbalances can cause breast tenderness, swelling, or changes in nipple sensitivity.
- Changes in appetite: Fluctuating hormones may lead to changes in appetite, such as increased food cravings or loss of appetite.
- Fatigue: Low hormone levels can contribute to feelings of fatigue or excessive sleepiness.
Emotional Symptoms:
- Mood swings: Hormonal changes can impact mood stability, leading to mood swings or heightened emotional sensitivity.
- Irritability: Decreasing hormone levels may contribute to feelings of irritability or a shorter temper.
- Anxiety or depression: Hormonal imbalances can also trigger symptoms of anxiety or depression in some women.
- Decreased libido: Fluctuating hormone levels may affect sexual desire or interest.
“It is important to note that experiencing these symptoms does not necessarily indicate a problem with the pregnancy. However, if you are concerned about your hormone levels or experiencing severe symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical advice.”
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms or have concerns about your hormone levels, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. They can evaluate your specific situation, provide appropriate guidance, and offer any necessary interventions to ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Effects of Low Hormone Levels on Pregnancy
Low hormone levels during pregnancy can have significant effects on the progress of the pregnancy. Hormone imbalances can impact various aspects, such as fertility, implantation, and early fetal development. It is crucial to manage hormone imbalances effectively to ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome.
When hormone levels are lower than normal, it can affect the ability to conceive. Imbalances in hormones such as progesterone and estrogen can disrupt the ovulation process and make it more challenging to get pregnant. Therefore, managing hormone imbalances becomes crucial for couples trying to conceive.
During early pregnancy, low hormone levels can affect the successful implantation of the fertilized egg in the uterus. Hormones play a vital role in preparing the uterine lining for implantation and sustaining the pregnancy. When hormone levels are low, the embryo may not be able to implant properly, increasing the risk of miscarriage.
Furthermore, hormone imbalances can have an impact on early fetal development. Hormones regulate various processes in the body and play a crucial role in the development of the fetus’s organs and systems. Insufficient hormone levels can interfere with proper fetal growth and development, potentially leading to birth defects or complications.
Managing hormone imbalances in pregnancy requires expert guidance and support from healthcare providers. They can assess hormone levels through blood tests, monitor the progression of the pregnancy, and recommend appropriate interventions if necessary.
Managing Hormone Imbalances in Pregnancy
To manage hormone imbalances during pregnancy, healthcare providers may prescribe medications or hormone replacement therapy to restore the hormone levels to normal. These interventions aim to support the overall health of the pregnancy and reduce the risk of complications.
Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can also help support hormone balance during pregnancy. Additionally, certain dietary supplements, such as folic acid and iron, may be recommended to support the body’s hormonal needs.
It is essential for expectant mothers to communicate openly with their healthcare providers about any concerns or symptoms related to hormone imbalances. Regular prenatal check-ups and monitoring of hormone levels can help ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.
| Effects of Low Hormone Levels on Pregnancy | Managing Hormone Imbalances in Pregnancy |
|---|---|
| – Impaired fertility | – Medications or hormone replacement therapy |
| – Increased risk of miscarriage | – Lifestyle modifications |
| – Impact on fetal development | – Dietary supplements |
| – Importance of healthcare provider guidance | – Open communication with healthcare providers |
Ways to Support Hormone Levels During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, maintaining healthy hormone levels is crucial for the proper development of both the mother and the baby. Hormonal imbalances can have various effects on pregnancy, including potential complications. To support optimal hormone balance, there are several strategies that expectant mothers can implement:
Lifestyle Changes:
1. Get Sufficient Rest: Adequate sleep is essential for hormone regulation. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night.
2. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt hormone levels. Engage in relaxing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
3. Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps regulate hormones and promotes overall well-being. Consult with your healthcare provider for exercise recommendations suitable for pregnancy.
Dietary Considerations:
1. Eat a Balanced Diet: Consume a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats.
2. Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water throughout the day to support hormone production and overall hydration.
3. Limit Processed Foods: Minimize the intake of processed and sugary foods, as they can disrupt hormone balance.
Supplements and Medications:
1. Prenatal Supplements: Taking prenatal vitamins as recommended by your healthcare provider ensures the adequate intake of essential nutrients for hormone regulation.
2. Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): In some cases, hormone replacement therapy may be necessary to maintain optimal hormone levels during pregnancy. This should only be done under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
It is important to note that every pregnancy is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial before making any significant changes to your lifestyle, diet, or incorporating supplements or medications.
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can support healthy hormone levels throughout your pregnancy, promoting the well-being of both you and your baby.
| Supporting Hormone Levels During Pregnancy | Description |
|---|---|
| Lifestyle Changes | Implement healthy habits such as getting sufficient rest, managing stress, and regular exercise. |
| Dietary Considerations | Eat a balanced diet, stay hydrated, and limit processed foods. |
| Supplements and Medications | Take prenatal supplements and consider hormone replacement therapy under medical supervision. |
Hormonal Fluctuations in the First Trimester
During the first trimester of pregnancy, hormonal fluctuations play a crucial role in sustaining and supporting the development of the fetus. Understanding these natural variations is essential for expectant mothers as they navigate the early stages of pregnancy.
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by the body that regulate various physiological processes. In the first trimester of pregnancy, several hormones undergo significant fluctuations to create an optimal environment for the growing baby. The key hormones involved in this process include:
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG): This hormone is produced by the placenta to support the early stages of pregnancy. It helps maintain the function of the corpus luteum, a temporary gland that produces progesterone. The levels of hCG rise rapidly during the first trimester, peaking around weeks 8 to 11, and then gradually decline.
- Progesterone: Progesterone is essential for maintaining the uterine lining and preventing premature contractions. During the first trimester, progesterone levels increase to support the implantation of the embryo and subsequent development.
- Estrogen: Estrogen levels also rise during the first trimester to promote blood flow to the uterus, stimulate breast tissue growth, and support fetal development.
It’s important to note that hormonal fluctuations in the first trimester can vary from woman to woman and even from pregnancy to pregnancy. Factors such as maternal age, overall health, and genetic predispositions can influence the extent and pattern of these fluctuations.
Common Concerns and Questions
Many expectant mothers have questions and concerns about the hormonal changes they experience during the first trimester. Here are some common queries addressed:
“Will hormonal fluctuations affect the progress of my pregnancy?”
While hormonal fluctuations are a natural part of pregnancy, extreme imbalances may have an impact. It’s important to regularly monitor hormone levels and seek medical advice if you have any concerns.
“Do hormonal fluctuations cause specific symptoms in the first trimester?”
Yes, hormonal changes can contribute to various symptoms, including morning sickness, mood swings, breast tenderness, and fatigue. These symptoms are typically transient and subside as hormone levels stabilize.
“Can I do anything to regulate my hormone levels during the first trimester?”
While hormonal fluctuations are a natural part of pregnancy, adopting a healthy lifestyle can help support hormonal balance. This includes eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, getting regular exercise, and managing stress levels.
By understanding the hormonal fluctuations that occur during the first trimester and addressing any concerns or questions, expecting mothers can navigate this transformative period with confidence and peace of mind.
Hormonal Changes and Miscarriage Risk
There is a significant link between hormonal changes and the risk of miscarriage. During pregnancy, hormone levels play a crucial role in supporting the development and maintenance of the pregnancy. Imbalances or fluctuations in hormone levels can potentially increase the likelihood of pregnancy loss. Understanding the impact of hormonal changes on the risk of miscarriage is essential for early detection and support.
Research has shown that certain hormone imbalances, such as low levels of progesterone, can be associated with an increased risk of miscarriage. Progesterone is a hormone that is vital for maintaining a healthy pregnancy. When progesterone levels are too low, it can hinder the implantation of the fertilized egg or contribute to early fetal loss. Detecting and addressing low progesterone levels early on can help reduce the risk of miscarriage.
In addition to progesterone, other hormonal changes can also affect the risk of miscarriage. Hormones like estrogen and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) play important roles in supporting pregnancy. Any disruption in their levels can impact the development and progression of the pregnancy.
If you suspect that you may have hormone imbalances during pregnancy, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can conduct hormone level tests and provide the necessary guidance and support.
Reducing Miscarriage Risk through Hormonal Support
Advancements in medical research and understanding of hormonal changes have led to various interventions and treatments aimed at reducing the risk of miscarriage. Hormonal support can help optimize hormone levels and provide a supportive environment for a healthy pregnancy.
This can involve hormone supplementation, such as progesterone therapy, to address low levels of specific hormones. Your healthcare provider may prescribe hormonal medications or recommend lifestyle changes to help rebalance hormone levels and minimize the risk of miscarriage.
| Ways to Reduce Miscarriage Risk through Hormonal Support | Description |
|---|---|
| Progesterone Supplementation | Additional progesterone may be prescribed to support pregnancy and prevent miscarriage, especially in cases of low progesterone levels. |
| Hormone Replacement Therapy | In certain cases, hormone replacement therapy may be used to address hormone imbalances and promote a healthy pregnancy. |
| Lifestyle Modifications | Healthier lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can help promote hormonal balance and decrease the risk of miscarriage. |
| Close Monitoring and Early Detection | Regular check-ups and monitoring of hormone levels can help identify any imbalances early on, allowing for timely intervention and support. |
A personalized approach is crucial when it comes to managing hormonal changes and reducing the risk of miscarriage. It is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best course of action based on your specific hormone levels and medical history.
By understanding the link between hormonal changes and miscarriage risk, women can be proactive in seeking appropriate support and interventions to optimize hormone levels and increase the chances of a successful pregnancy.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing pregnancy hormone levels is crucial for a healthy pregnancy journey. As we have explored in this article, hormonal changes and imbalances can significantly impact the progression of pregnancy and increase the risk of miscarriage.
By being aware of the symptoms of decreasing hormone levels, women can seek timely medical advice and support to manage hormone imbalances. Consulting with healthcare providers is essential for personalized guidance on ways to support hormone levels during pregnancy.
It is important to remember that fluctuations in pregnancy hormone levels are a natural part of the first trimester. While there may be concerns about the risks of miscarriage associated with hormonal changes, ongoing research and medical advancements aim to address and reduce these risks.
Overall, understanding the relationship between pregnancy hormone levels, managing hormone imbalances, and minimizing miscarriage risk is key to providing reassurance and support to women on their pregnancy journey. With the right knowledge, resources, and guidance, women can navigate through the fluctuations in their hormone levels and optimize their chances of a healthy pregnancy outcome.
FAQ
How do dropping pregnancy hormone levels affect the pregnancy?
Dropping pregnancy hormone levels can have various effects on the pregnancy. Low hormone levels may be associated with a higher risk of miscarriage and can impact fertility, implantation, and early fetal development. However, it’s important to note that hormone fluctuations are a normal part of early pregnancy, and healthcare providers can often manage hormone imbalances to support a healthy pregnancy.
What hormonal changes occur during early pregnancy?
Early pregnancy is marked by significant hormonal changes. The levels of hormones such as human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), progesterone, and estrogen increase to support the pregnancy. However, these hormone levels can also fluctuate, and some women may experience a decrease in hormone levels during this time. Various factors, such as implantation failure or an ectopic pregnancy, can contribute to declining hormone levels.
What are the symptoms of decreasing hormone levels during pregnancy?
Symptoms of decreasing hormone levels can vary among individuals, but common signs include a decrease in breast tenderness, a decrease in nausea or morning sickness, and a decrease in the intensity of pregnancy-related symptoms. Changes in mood, such as a decrease in irritability or emotional lability, can also occur. It’s important to note that these symptoms alone do not confirm declining hormone levels, and it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
How do low hormone levels affect a pregnancy?
Low hormone levels during pregnancy can impact the progress of a pregnancy. Hormone imbalances can affect the fertilization of eggs, the implantation process, and the early development of the fetus. However, healthcare providers have strategies to manage hormone imbalances in pregnancy and may recommend specific treatments or interventions to support hormone levels and optimize the chances of a successful pregnancy outcome.
What are some ways to support hormone levels during pregnancy?
There are several ways to support healthy hormone levels during pregnancy. This includes maintaining a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, particularly those that support hormone production. Engaging in regular physical activity, reducing stress levels, and getting enough sleep can also contribute to hormonal balance. In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend hormone supplements or medications to help manage hormone imbalances.
How do hormonal fluctuations occur in the first trimester?
Hormonal fluctuations commonly occur during the first trimester of pregnancy. The levels of hormones such as hCG, progesterone, and estrogen can rise and fall during this period. Fluctuations are normal and are generally associated with the changing needs of the developing embryo and placenta. However, if there is a significant drop in hormone levels, it is vital to consult with a healthcare provider to evaluate any potential concerns.
Are there hormonal changes that increase the risk of miscarriage?
Yes, certain hormonal changes can increase the risk of miscarriage. Hormone imbalances, such as low progesterone levels or an inadequate rise in hCG, can impact the viability of the pregnancy. It’s essential to address hormone imbalances early in pregnancy and work closely with a healthcare provider to optimize hormone levels and minimize the risk of miscarriage.
What are the key takeaways about dropping pregnancy hormone levels?
Understanding and managing hormone levels during pregnancy is crucial for a healthy pregnancy outcome. While hormone fluctuations are a natural part of early pregnancy, it’s essential to pay attention to any symptoms of declining hormone levels and seek medical advice if necessary. Healthcare providers have strategies to support hormone levels, and ongoing research aims to reduce the risk of miscarriage associated with hormonal changes. Remember, you don’t have to navigate these fluctuations alone, and support is available to help you have a healthy pregnancy.