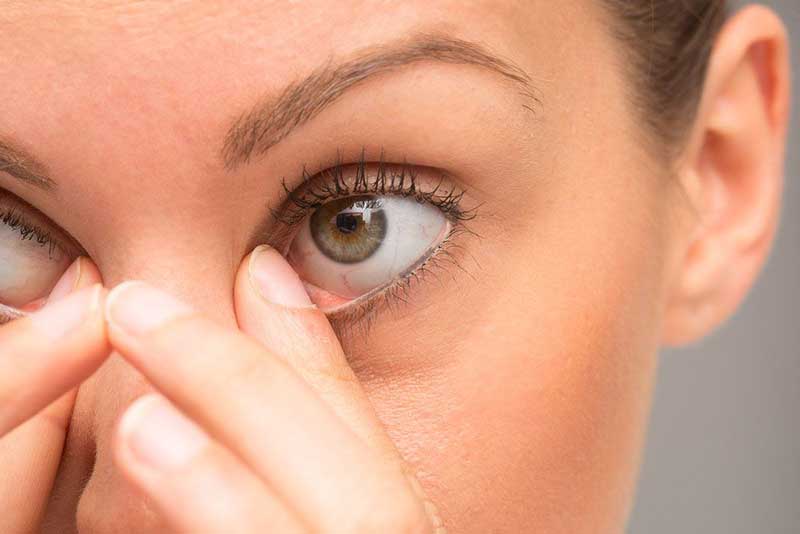
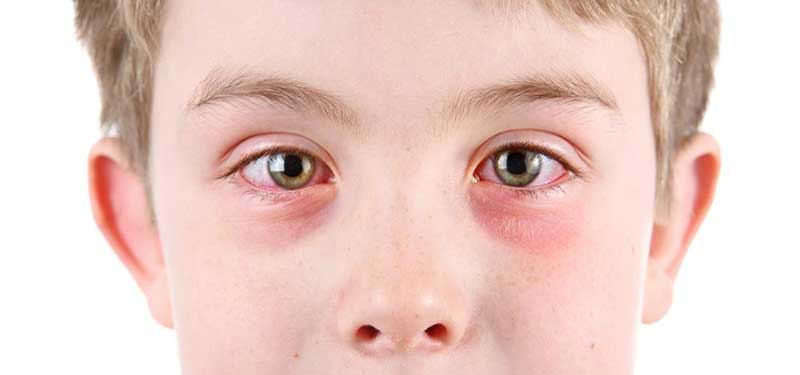
Eye inflammation, also known as ocular inflammation or uveitis, is a common condition that affects many individuals. It refers to the inflammation of the uvea, which is the middle layer of the eye that consists of the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. This condition can lead to discomfort, pain, and even vision loss if left untreated. In order to effectively manage eye inflammation, it is important to understand its causes and take appropriate measures. opposingdigits will explore the various causes of eye inflammation and provide insights on how to prevent and treat this condition.
Introduction
The human eye is a complex organ responsible for vision, and any inflammation in its structures can disrupt its normal functioning. Eye inflammation can occur due to various reasons, including infections, autoimmune disorders, allergies, trauma, or exposure to chemicals. Understanding the causes behind eye inflammation is crucial in order to identify the appropriate treatment and prevent complications.
Anatomy of the Eye
Before delving into the causes of eye inflammation, it is essential to have a basic understanding of the eye’s anatomy. The eye consists of several components, including the cornea, iris, lens, retina, and the uvea. The uvea is the middle layer of the eye, comprising the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Inflammation of the uvea, known as uveitis, is a common form of eye inflammation.
What is Eye Inflammation?
Eye inflammation, or uveitis, refers to the swelling and irritation of the uvea. It can affect one or both eyes and may lead to various symptoms such as redness, pain, blurred vision, light sensitivity, and floaters. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for effective management and treatment.
Common Causes of Eye Inflammation
Infections
Infections caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites can lead to eye inflammation. Common infectious causes include conjunctivitis, herpes simplex virus, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, and tuberculosis. Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment are necessary to prevent the infection from spreading and causing further complications.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own tissues. Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, sarcoidosis, and Behçet’s disease can cause eye inflammation. Proper management of the underlying autoimmune condition is crucial in reducing the frequency and severity of eye inflammation episodes.
Allergies
Allergic reactions to pollen, dust mites, pet dander, or certain medications can trigger eye inflammation. This condition, known as allergic conjunctivitis, often presents with redness, itching, and watery eyes. Avoiding allergens and using antihistamine eye drops can provide relief and prevent inflammation.
Trauma or Injury
Direct trauma to the eye, such as a blow or penetrating injury, can result in eye inflammation. This can lead to significant pain, swelling, and vision problems. Seeking immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent further damage and manage the inflammation effectively.
Chemical Exposure
Exposure to chemicals or irritants, such as cleaning solutions or industrial substances, can cause eye inflammation. It is important to use protective eyewear and take necessary precautions when working with hazardous materials to minimize the risk of eye irritation and inflammation.
Systemic Diseases
Certain systemic conditions, including sarcoidosis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease, can manifest as eye inflammation. Proper management of these underlying diseases is essential to prevent complications and maintain overall eye health.
Medications
Some medications, such as bisphosphonates, antibiotics, and certain diuretics, may cause eye inflammation as a side effect. It is important to inform your healthcare provider about any medications you are taking to assess their potential impact on eye health.
Complications from Eye Surgery
Eye inflammation can occur as a complication of eye surgery, such as cataract surgery or refractive surgery. Surgeons take precautions to minimize the risk, but in some cases, inflammation may still develop. Close monitoring and appropriate post-operative care can help manage the inflammation effectively.
Idiopathic Causes
In some cases, the exact cause of eye inflammation may remain unknown. These cases are referred to as idiopathic uveitis. While the cause may be uncertain, treatment options are available to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
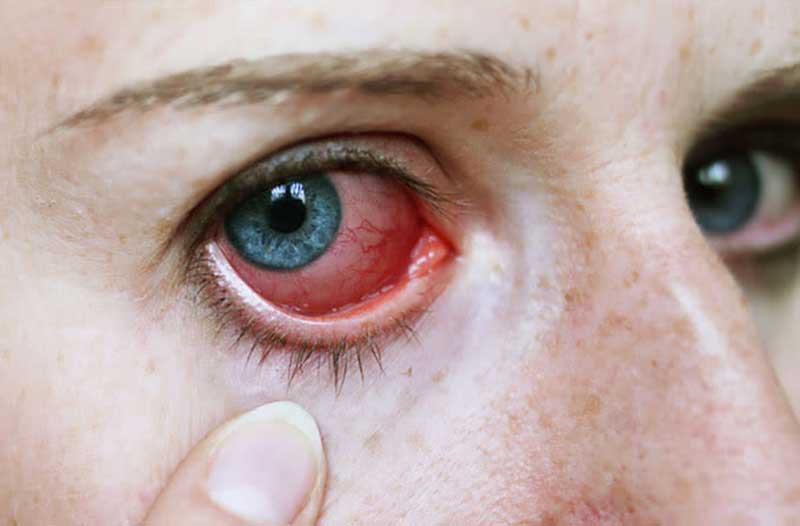
Symptoms of Eye Inflammation
The symptoms of eye inflammation can vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common symptoms include redness, eye pain, blurred vision, light sensitivity, floaters, and increased tearing. Prompt medical attention is advised if these symptoms persist or worsen.
Diagnosing Eye Inflammation
Diagnosing eye inflammation involves a comprehensive eye examination, medical history review, and potentially additional tests. These may include visual acuity tests, slit-lamp examination, tonometry, and laboratory tests to determine the cause and severity of the inflammation.
Treatment Options for Eye Inflammation
The treatment approach for eye inflammation depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient factors. Treatment options may include:
Medications
Anti-inflammatory medications, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and manage symptoms. These medications can be administered orally, topically, or through injections.
Eye Drops
Eye drops containing corticosteroids or other anti-inflammatory agents are often used to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation. Proper application techniques and adherence to the prescribed dosage are crucial for optimal effectiveness.
Steroid Injections
In severe cases of eye inflammation, corticosteroid injections may be administered directly into the eye. This targeted approach helps deliver a high concentration of medication to the affected area, providing rapid relief.
Surgery
In certain situations, surgery may be necessary to manage eye inflammation. Surgical procedures can range from removing scar tissue to correcting complications caused by inflammation. Close collaboration with an experienced ophthalmologist is essential in determining the most appropriate surgical intervention.
Lifestyle Changes
Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage eye inflammation. These include getting sufficient rest, adopting a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, avoiding smoking, protecting the eyes from excessive sunlight, and practicing good hygiene.
Prevention Tips for Eye Inflammation
While some causes of eye inflammation cannot be prevented, there are measures you can take to minimize the risk. These include:
- Practicing good hygiene and avoiding touching your eyes with dirty hands
- Using protective eyewear when engaging in activities that may cause eye trauma
- Keeping your environment clean and free from irritants
- Managing underlying systemic conditions through regular medical check-ups and appropriate treatment
- Following your eye care professional’s advice on contact lens hygiene and usage
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience persistent or worsening symptoms of eye inflammation. Prompt diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and preserve your vision. Contact your eye care professional if you have any concerns or questions about your eye health.
Conclusion
Eye inflammation, or uveitis, can significantly impact an individual’s vision and quality of life if left untreated. By understanding the various causes of eye inflammation and implementing preventive measures, it is possible to reduce the risk of developing this condition. Regular eye examinations, prompt medical attention, and adherence to prescribed treatments are crucial for maintaining optimal eye health.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Can eye inflammation cause permanent vision loss?
While eye inflammation can lead to vision loss if left untreated, timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help prevent permanent damage and preserve vision.
Can allergies cause eye inflammation?
Yes, allergies can cause eye inflammation, commonly known as allergic conjunctivitis. Avoiding allergens and using antihistamine eye drops can help alleviate symptoms.
How is eye inflammation diagnosed?
Diagnosing eye inflammation involves a comprehensive eye examination, medical history review, and potentially additional tests to determine the underlying cause and severity.
Is eye inflammation contagious?
No, eye inflammation itself is not contagious. However, certain infectious causes of eye inflammation, such as conjunctivitis, can be contagious.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent eye inflammation?
Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle, practicing good hygiene, and protecting the eyes from potential irritants and trauma can help minimize the risk of eye inflammation.